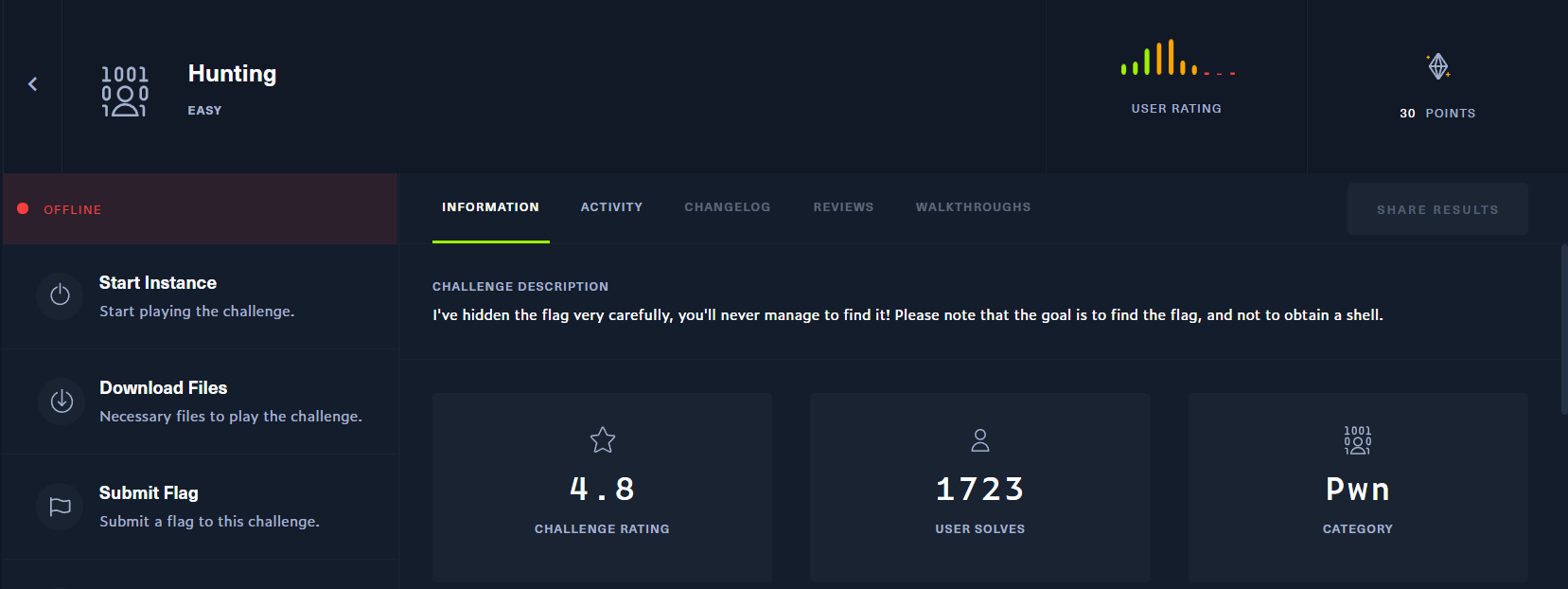
Analyzing the binary
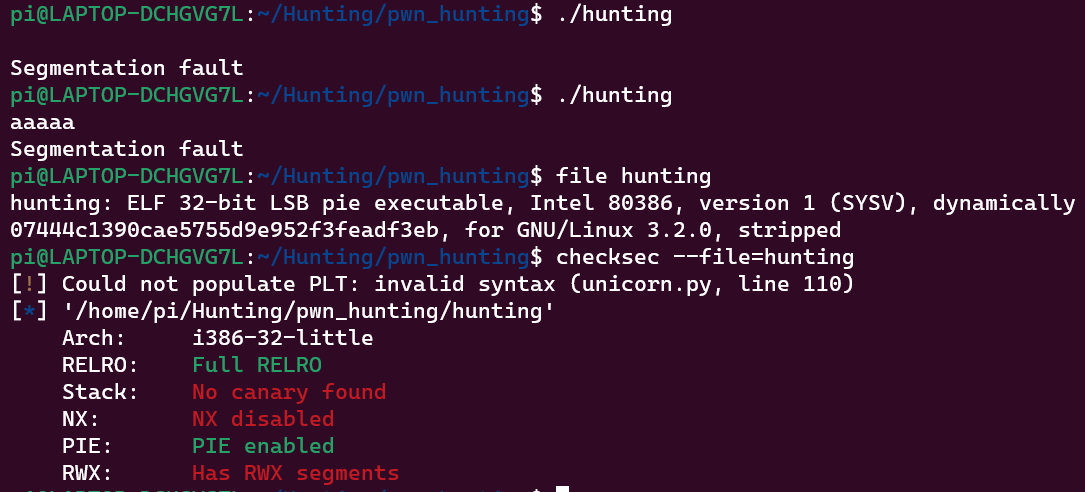 The binary haults for the input and crashes as we pass something.
The binary haults for the input and crashes as we pass something.
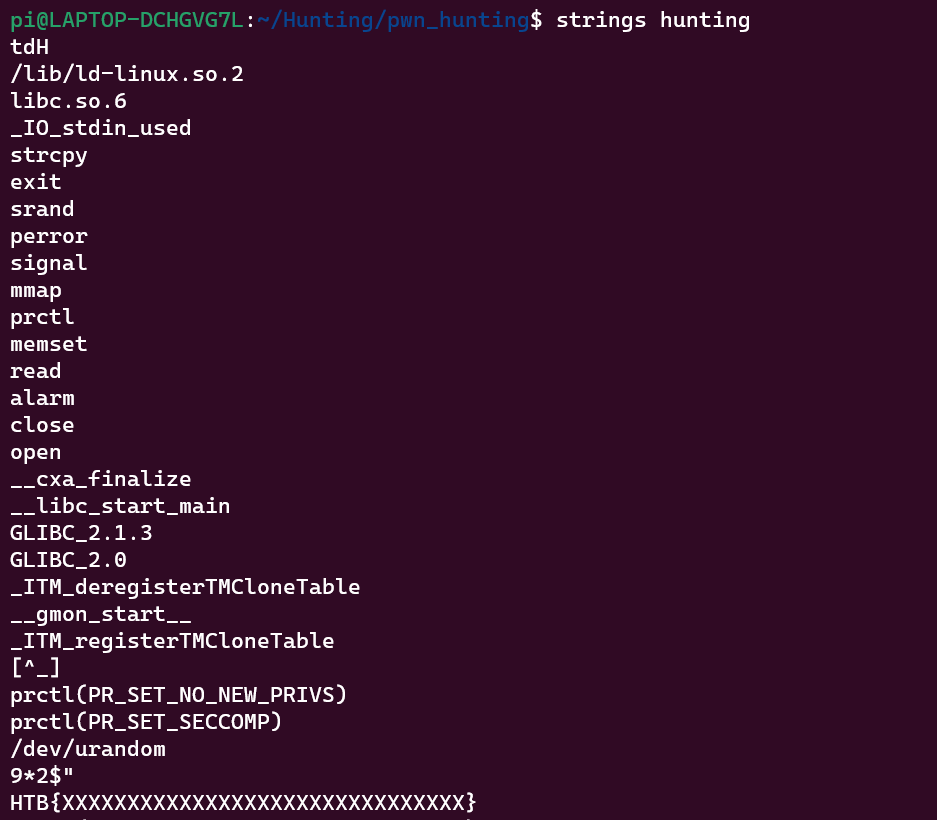 Upon reading the stings we found a string which looks like a dummy file. Time to look for it in IDA pro.
Upon reading the stings we found a string which looks like a dummy file. Time to look for it in IDA pro.
IDA
i changed some of the variable names for better understanding
I jumped to the variable to see where it was being used and after reading the code we see that that string was being moved from one location to another.
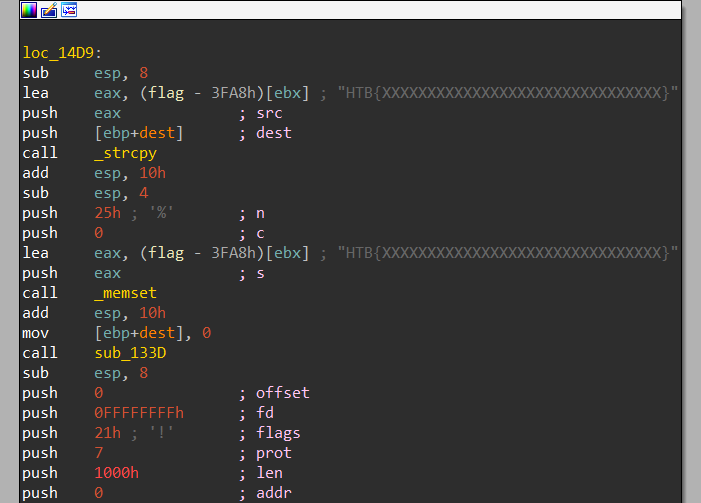 It first sets a new location and copies the flag to that location then empty’s flag value from the previous location.
It first sets a new location and copies the flag to that location then empty’s flag value from the previous location.
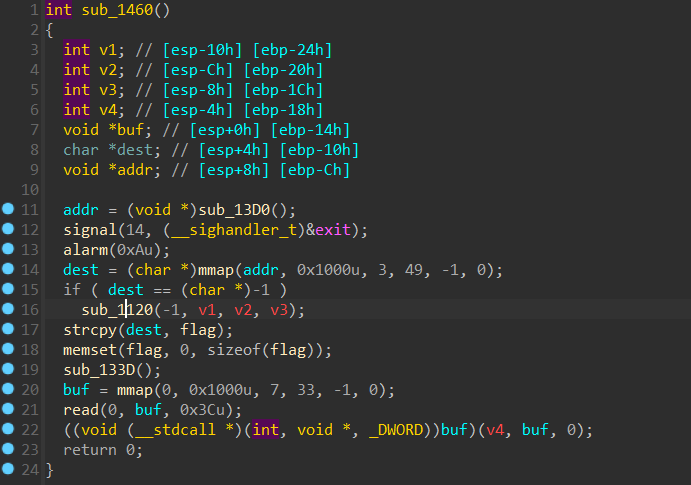 It also creates an exit signal and triggers it with a timer of 10 seconds. Which means that program will exit after 10 seconds.
It also creates an exit signal and triggers it with a timer of 10 seconds. Which means that program will exit after 10 seconds.
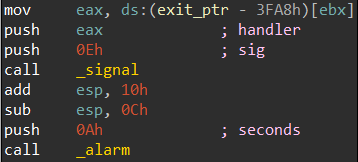
I am literally reversing it from down to top
Before the singnal code, it calls a function which returns a randomly generated number.
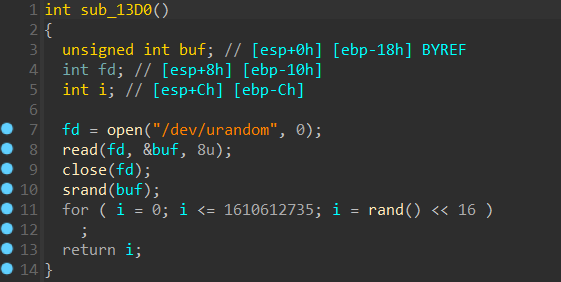 Further reading the code we now know that it generates a number from a range of
Further reading the code we now know that it generates a number from a range of 0x5FFFFFFF < i <= 0xF7000000
which is a randomly generated address.
Then it takes to a buffer size of 60 and executes it as a shellcode. (reason why the segfault)
So overall the program moves the flag to a random address location, kills the program after 10 seconds, reads our input and executes it as a shellcode.
NOTE: Since the buffer size is limited. We have to be very creative and minimal while crafting our payload.
Planning our exploit
Since the program kills itself after 10 seconds we will set up a timer with much higher value. Then we will traverse through addresses from a range of 0x5FFFFFFFsearching for the flag and send it to stdout if it matches.
| |
Pwn Time
First we craft our payload into bytecodes and send it through pwntools

| |
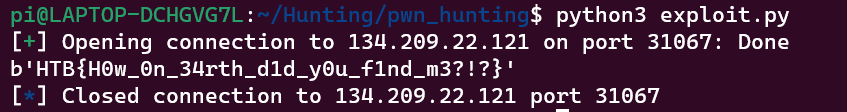
Flag: HTB{H0w_0n_34rth_d1d_y0u_f1nd_m3?!?}